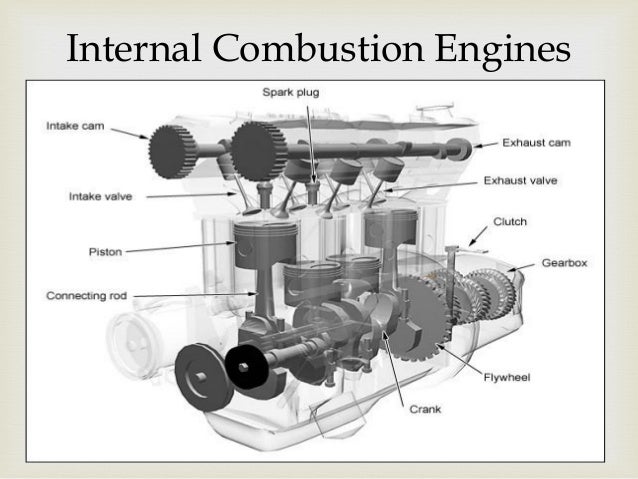
An internal combustion engine (ICE) is a heat engine where the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the
working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine the expansion of
the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies
direct force to some component of the engine. The
force is applied typically to pistons, turbine
blades, rotor or a nozzle.
This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical
energy into useful mechanical
energy.
The first
commercially successful internal combustion engine was created by Étienne
Lenoir around 1859 and the first modern
internal combustion engine was created in 1876 by Nikolaus Otto (see Otto engine).
The term internal combustion engine usually refers to an engine in which
combustion is intermittent, such as the more familiar four-stroke and two-stroke piston engines, along with variants,
such as the six-stroke piston engine and the Wankel rotary
engine. A second class of internal combustion engines use continuous
combustion: gas turbines, jet engines and most rocket
engines, each of which are internal combustion engines on the same
principle as previously described. Firearms are
also a form of internal combustion engine.
Internal
combustion engines are quite different from external combustion engines, such as steam or Stirling
engines, in which the energy is delivered to a working fluid not
consisting of, mixed with, or contaminated by combustion products. Working
fluids can be air, hot water, pressurized water or even liquid sodium, heated in a boiler.
ICEs are usually powered by energy-dense fuels such as gasoline or diesel,
liquids derived from fossil fuels.
While there are many stationary applications, most ICEs are used in mobile
applications and are the dominant power supply for vehicles such as cars, aircraft, and boats.
Typically
an ICE is fed with fossil fuels like natural gas or petroleum products such as gasoline, diesel fuel or fuel oil.
There is a growing usage of renewable
fuels like biodiesel for compression ignition engines and bioethanol or methanol for spark ignition engines. Hydrogen is sometimes used, and can be made
from either fossil fuels or renewable energy.